FORWARD FOODING
THE BLOG
How Ozempic is Changing Food Personalization

As Ozempic transforms the way we manage weight and nutrition, the food industry is facing an unprecedented challenge—how to keep up with consumers who are eating differently. With fewer cravings and reduced caloric intake, thanks to Ozempic’s appetite-suppressing effects, traditional food products like snacks, fast food, and high-calorie meals are losing appeal. This shift is pushing companies to explore new frontiers in health-focused, personalized nutrition. Could this be the push the food industry needs to fully embrace functional, low-calorie options that support wellness goals? The food industry is undeniably in for a major transformation.
Understanding Food Personalization
Food personalization tailors diets and meal plans to individual nutritional needs and preferences, considering factors like age, genetics, lifestyle, and health conditions. And as consumers become more health-conscious, the demand for tailored nutrition has surged. According to a survey conducted by Deloitte, three in four modern consumers actively seek personalized nutrition products and services that align with their unique lifestyles and health goals.
In recent years, the landscape of food personalization has been rapidly evolving, driven by advances in technology, genetics, and a deeper understanding of individual nutritional needs. One of the most intriguing developments in this space is the emergence of Ozempic, a medication initially designed to treat Type 2 diabetes, which is now being recognized for its potential to transform how we approach personalized nutrition.
Ozempic: Beyond Diabetes Management
Ozempic, a brand name for semaglutide, is a glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist introduced to help manage blood sugar levels in people with Type 2 diabetes. It mimics the effects of the GLP-1 hormone, which regulates blood sugar by stimulating insulin secretion and reducing glucagon levels. However, Ozempic’s secondary effect on appetite regulation and weight loss is particularly interesting. It slows down gastric emptying, meaning the food remains in the stomach for a longer period, leading to an extended feeling of fullness. It’s a similar effect to weight loss surgery, where the stomach is physically reduced in size. However, with these medications, the stomach isn’t actually smaller—it just feels that way because the food takes longer to digest.
One study has shown that Ozempic can significantly reduce appetite and promote weight loss, even in individuals without diabetes. This has led to its off-label use as a weight management tool, opening new possibilities for food personalization. By influencing appetite and food intake, Ozempic could become a key component in personalized diet plans, helping individuals manage their weight and nutritional intake more effectively.
The rise in GLP-1 medication use has led to changes in consumer eating habits, affecting their overall consumption of packaged foods and snacks. Sweden Foodtech founder Johan Jörgensen wrote his own experience in taking the medication, indicating that he has seen significant results as early as three months. He calls the whole process effortless with effects that profoundly shifted his food habits – eating 25% less, losing cravings for snacks and interest in heavy foods like beef and cheese, and increasing his intake of fruits and vegetables.
Jörgensen’s anecdotal experience aligns with the results of the study by Morgan Stanley. The study found that people who have taken anti-obesity medications (AOM) like Ozempic have seen a boost in consumption in healthier categories while decreasing consumption of food categories that are high in calories, sugar, and salt such as confections, sugary drinks, alcohol, and salty snacks. In a study by Mattson, some AOM users consumed fewer animal-based proteins and were “particularly turned off” especially with beef.
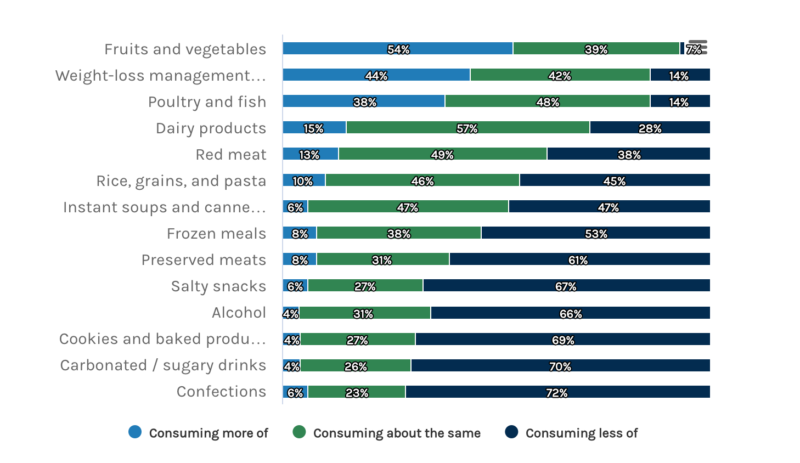
Healthier categories see a boost in consumption by AOM users (Source: Morgan Stanley)
Shifts in food consumption patterns mean shifts in spending habits as well. In a survey in the U.S. by Numerator, early trends show that households with GLP-1 users are cutting back on food and alcohol purchases more compared to non-GLP-1 users. The data also shows that when GLP-1 users stop taking the medication, their monthly household spending returns to previous levels.
According to the study by Morgan Stanley, decreasing appetite brought by GLP-1 medications could reduce calorie intake by 2-% to 30% daily. Pamela Kaufman, Morgan Stanley’s Tobacco and Packaged Food Analyst, said, “Companies will likely adapt to changes in consumer behaviour through innovation and by reshaping their product portfolios.” Here’s how Ozempic and other GLP-1 drugs could reshape the food industry:
- Packaged Food Sector: Consumption of snacks like confectionery, baked goods, and salty snacks is forecasted to decline by up to 3% by 2035 due to increased use of obesity drugs.
- Snack Food Segment: The frequency of snacking decreases after patients begin using obesity drugs, with 74% of users eating fewer snacks.
- Health and Weight Management Foods: Demand for weight-loss management products, such as protein shakes and meal replacement bars, is expected to grow as consumers seek healthier alternatives.
- Beverage Industry: Obesity drug users are cutting back on sugary drinks and alcohol, with 65% reducing soda consumption and 62% drinking less alcohol, potentially leading to a 2% drop in alcohol consumption by 2035.
- Restaurant and Fast Food Sector: Chains offering less healthy food options may experience a 1-2% drop in same-store sales growth. Fast casual chains may adapt with healthier menu options, while others, such as pizza and fried-chicken chains, face more risk due to limited menu flexibility.
- Grocery Retailers: The impact on traditional grocery stores may be modest in the short term, but as obesity drug usage rises, conventional grocers may face increasing challenges, while mass retailers offering a broader range of products could be better insulated.
In response to these challenges, food companies are exploring several strategies:
- Product Reformulation: Companies are reformulating products to cater to health-conscious consumers and align with new dietary trends.
- Innovation in Health-Conscious Products: There is an increased focus on developing new products that meet the demands of a market looking for functional, nutritious options.
- Diversification: Some companies are diversifying their portfolios to include more health-oriented and low-calorie options that can appeal to consumers affected by appetite suppression from GLP-1 medications.
Ozempic’s disruption to the food industry is so significant that Big Food company Nestlé has introduced a new platform dedicated to GLP-1-related technology aimed at advancing weight management and metabolic health solutions. Nestlé also launched a new line of $5 pizza sandwiches specifically targeting users of weight loss drugs such as Wegovy and Ozempic, who experience reduced appetite and altered eating habits. Nestlé’s efforts are anticipated to lead to the creation of new products that could serve as alternatives or complements to current GLP-1 medications.
Meanwhile, Kellogg’s has rebranded to Kellanova, in response to the changing market dynamics, placing a stronger emphasis on snacking products. The company plans to innovate and expand its snack offerings, aiming to appeal to health-conscious consumers who are looking for convenient, healthier snack options.
With these recent developments from just two massive food companies, it’s clear that the rise of GLP-1 drugs is expected to bring even more significant and rapid changes to our food systems. This could present both challenges and opportunities for the food industry to innovate and swiftly adapt to evolving consumer behavior and new dietary trends. In an interview with Mattson Chief Innovation and Marketing Officer, Barb Stuckey, she indicates that the opportunities for traditional food manufacturers could come in the form of creating smaller portions, reducing sodium content, and increasing nutrition content. She also said that this is the perfect time for the food industry to reset their strategies.
Companies in the GLP-1 Space
The global digital health market for obesity is expected to rise from $47.5B in 2023 to $457.4B by 2034. This growth is driven by advancements in digital health technologies like apps, wearables, and telemedicine to address the global obesity epidemic. The market expansion is fueled by increasing obesity rates, rising healthcare costs, and consumer demand for personalized health management solutions that integrate digital platforms to monitor weight and lifestyle changes.
According to recent figures from our FoodTech Data Navigator, there are 175 startups in the weight management space, which have raised a total of $4.7B in funding, with $1.8B of the investment raised was from 2021 alone. Technologies in the space encompass a wide range of innovations, including meal-planning tools, grocery shopping assistants, low-calorie food products, and nutrition-tracking apps.
Michael Siluk/Getty Images; iStock
One company transforming the food personalization space is Novo Nordisk, the maker of Ozempic and Wegovy. Similar to Ozempic, Wegovy’s active ingredient is also semaglutide. However, this medication is specifically prescribed for weight management in adults with obesity or overweight conditions.
Ro is also making GLP-1 medications easily available to more consumers. As part of its Body Program, Ro launched the GLP-1 Supply Tracker to help consumers with real-time insights on GLP-1 drug shortages and supply alerts, while its GLP-1 Insurance Coverage Checker aids people in finding out if their insurance covers treatment with GLP-1 medications.
Another New York-based telehealth company focusing on weight management is Calibrate. It offers a unique program that combines FDA-approved medications alongside personalized lifestyle coaching. The company focuses on “metabolic reset,” which combines medication with four key pillars: food, exercise, sleep, and emotional health.
Meanwhile from Boston, Form Health telehealth company specializing in science-based obesity care. It offers personalized care plans created by the American Board of Obesity Medicine (ABOM)-certified physicians and registered dietitians. These plans include lifestyle changes and FDA-approved medications when necessary.
EraCal Therapeutics, a Swiss biotech company founded in 2018, is focused on developing innovative anti-obesity drugs. The company’s lead asset, Era-379, is an oral small-molecule therapy, which has showed promising results in reducing weight in obese mice by over 20% in just two weeks and could potentially offer a novel approach to tackling obesity through safer and more effective treatments.
Canada-based Metaphore Biotechnologies harnesses biomimicry and machine learning to unlock the transformative therapeutic potential of functional molecular mimics. Through its innovative MIMIC platform, and a partnership with Novo Nordisk, Metaphore aims to develop next-gen therapeutics for obesity management, to create long-acting agents that will require infrequent dosing.
ProFound Therapeutics, based in Massachusetts, is a biotechnology company focused on developing innovative therapies for serious diseases. Because of the company’s ProFoundry Platform, which explores proteins’ therapeutic potentials, Pfizer recently announced a collaboration with ProFound to identify novel first-in-class meications for the treatment of obesity.
Metsera, a New York-based biopharmaceutical company, is dedicated to developing cutting-edge treatments for obesity and metabolic diseases. The company aims to deliver next-generation medicines through a varied portfolio of oral and injectable therapies, addressing the increasing need for effective weight loss solutions in a dynamic market.
Case Studies
Case Study #1: GLP-1Nutrition by Nestlé Health Science

Focus: Comprehensive Nutrition Support
Nestlé Health Science has developed a comprehensive nutrition support platform tailored for people using GLP-1 medications. The platform, GLP-1Nutrition, offers a range of expert-guided nutritional solutions designed to complement the weight loss and appetite-suppressing effects of GLP-1 therapies.
Key Features:
- Medical nutrition solutions targeted at those on GLP-1 treatments
- Expert-led programs for sustainable weight management
- Balanced meal plans aimed at optimizing metabolic health and energy
Case Study #2: Daily Harvest

Focus: Personalized “Companion Meal” Solutions
Daily Harvest’s Companion Food Collection offers personalized meal options for individuals using GLP-1 therapies like Ozempic. By focusing on nutrient-dense, plant-based meals, the company addresses the unique needs of users undergoing weight management therapies. Their meals are designed to complement GLP-1 medications by maintaining balanced nutrition while promoting healthy eating habits.
Key Features:
- Tailored plant-based ingredients
- Convenient, ready-to-eat or blend meals
- Emphasis on supporting metabolic health and long-term wellness goals
Case Study #3: Berry Street

Focus: Personalized Dietary Support for GLP-1 Users
Berry Street provides a personalized approach to nutrition for individuals on GLP-1 medications. Their platform offers guided support in meal planning and nutritional strategies, tailored to help individuals using drugs like Ozempic achieve their health and wellness goals more effectively.
Key Features:
- Customized dietary plans for GLP-1 users
- Continuous nutritional guidance to ensure balanced intake
- Support in managing side effects and achieving long-term goals
Case Study #4: Supergut

Focus: Gut Health Using Natural Alternatives to GLP-1 Treatment
Supergut markets itself as “Natural Ozempic”, underscoring the benefits of prebiotic fiber in stimulating GLP-1 hormones and mimic the appetite-suppressing and blood sugar-regulating effects of GLP-1 drugs, providing a natural, functional food solution. As GLP-1 medications gain popularity, Supergut has strategically positioned itself at the forefront of the “natural GLP-1” movement. With a surge in retail expansion through major partnerships like GNC, the brand emphasizes the growing consumer demand for natural alternatives to pharmaceutical GLP-1 treatments. Supergut’s marketing appeals to health-conscious consumers who are looking for sustainable, natural weight management solutions.
Key Features:
- Products include fiber-rich shakes, bars, and supplements (aided by a personalized nutrition quiz to help users choose the right products that match their health goals)
- Clinically proven to boost GLP-1 hormone production naturally
Conclusion
The surge in GLP-1 medication use signals a transformative shift in the food industry, impacting food personalization in response to changing consumer priorities. Companies are adapting by innovating their offerings through healthier product options or complementary services that align with new consumer preferences and needs. This evolution highlights the increasing importance of personalization in addressing modern wellness goals and changing market demands. The strategic responses of early movers in the industry suggest that personalized nutrition is becoming a key focus, setting the stage for broader industry-wide changes in food offerings and consumer engagement.
If you’re interested in learning more about functional foods, personalization trends, and other areas of FoodTech, check out the Food Data Navigator and book a free demo today!
Forward Fooding is the world’s first collaborative platform for the Food & Beverage industry via FoodTech Data Intelligence and Corporate-Startup Collaboration – Learn more about our Consultancy and Scouting Services and our Startup Network.
Follow us
Sponsored Articles
9 July 2025
Forward Fooding celebrates the selection of 12 pioneering startups for the inaugural pladis Accelerator Programme. From water lily popcorn to sugar-converting enzymes, these innovations represent the future of snacking, addressing obesity, sustainability, and personalized nutrition through cutting-edge food technology.
21 March 2025
Tim Ingmire, VP of Global Innovation & Technology at pladis, discusses how the snacking giant is supporting early-stage startups in foodtech, health, and sustainability through their accelerator program. Learn about their focus on personalized nutrition, functional foods, and future ingredients to bring innovative, delicious products to consumers worldwide.
8 February 2024
Future Food-Tech returns to San Francisco on March 21-22 Over 1,700 food-tech leaders, from CPG brands, retailers, ingredient providers, [...]
1 February 2023
The 4th edition of FoodTech 500 is taking off and we are excited to partner with NEOM for the third consecutive year to support the best international AgriFoodTech entrepreneurs.
10 February 2022
One of the elements we enjoy the most here at Forward Fooding about working with AgriFoodTech startups is being [...]







