FORWARD FOODING
THE BLOG
From Waste to Value: Sustainable Ingredients & Circularity Transforming Food Systems

In a world seeking more sustainable food systems, the transformation of what was once considered “waste” into valuable ingredients and products represents one of the most promising frontiers of innovation. At Forward Fooding, we’re witnessing an exciting evolution in how technology is creating circular food economies that maximise resource efficiency and minimise environmental impact by finding new value in previously discarded materials, challenging conventional production models, and reimagining our relationship with food resources.
The Food Waste Crisis & Market Opportunity
The numbers tell a sobering story. According to the latest UN FAO data, approximately 1.3 billion tonnes of food are wasted globally each year, representing an economic loss of approximately $400B. This waste occurs at every stage of the food supply chain – from farm fields to processing facilities, retail shelves, and our kitchen bins.
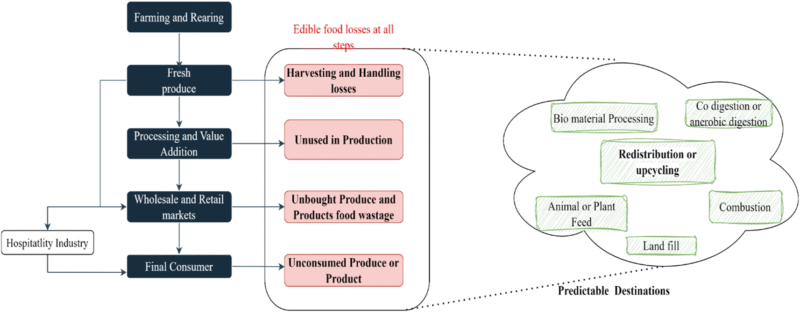
Food losses at different stages of the food value chain. Source
Beyond the economic implications, food waste represents a substantial environmental challenge. The United States alone discards nearly 60 million tons of food annually—almost 40% of its entire food supply. This material ranks as the number one contributor to waste in US landfills, accounting for 24.1% of all municipal solid waste.
Yet within this challenge lies a tremendous opportunity for circular innovation through upcycling specific food categories. According to 2022 data, 31.3 million tons of produce, 18 million tons of prepared foods, 14.2 million tons of dairy and eggs, 10.6 million tons of dry goods, and 5.08 million tons of fresh meat and seafood could potentially be upcycled. These materials include damaged produce, by-products, and scraps from food preparation that would otherwise not be suitable for human consumption but can be transformed into valuable ingredients. The market for these upcycled materials and ingredients is projected to grow substantially as brands increasingly seek sustainable ingredients with compelling origin stories.
Upcycling: Transforming Byproducts into Premium Ingredients
At the heart of the circularity movement is the reimagining of “waste” streams as valuable resources. Innovative companies are converting byproducts like spent grains, fruit pomace, vegetable trimmings, and even coffee grounds into nutritious flours, plant-based proteins, functional fibers, and bioactive compounds that command premium prices.
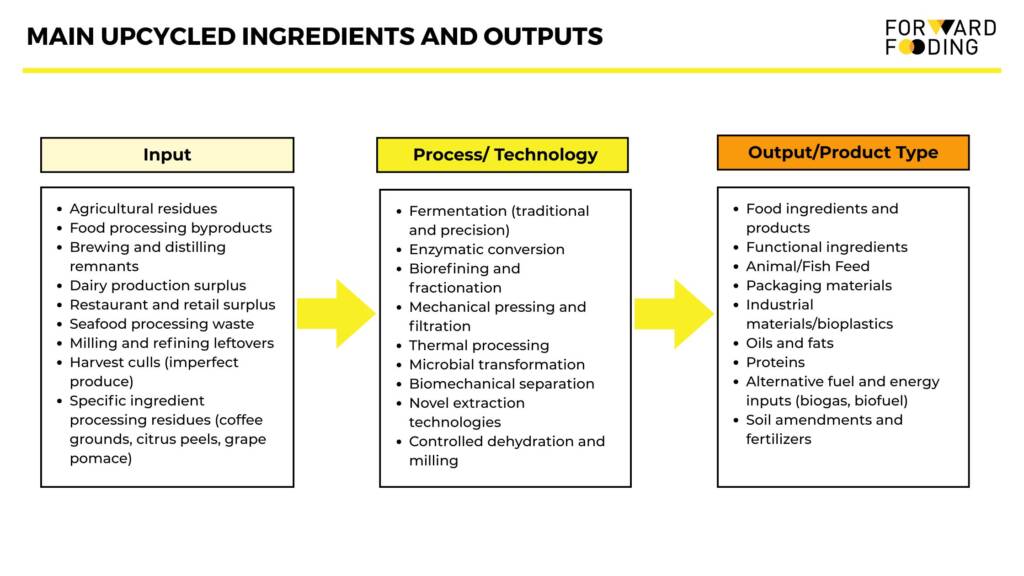
This upcycling approach creates entirely new value streams from materials that were previously discarded. What makes these ingredients particularly compelling is their dual benefit: they often have impressive nutritional and functional properties while significantly reducing the environmental footprint compared to conventional ingredients.
Investment Landscape
The investment community has taken notice of the circular ingredients sector. Our FoodTech Data Navigator counts about 480+ companies worldwide working with upcycling processes, having raised collectively $5B+ over time, with a peak year of $1.6B raised in 2023.
This sector is also benefiting from robust financial and regulatory incentives:
- The United States has enhanced tax deductions for businesses that donate food, allowing deductions of up to 15% of taxable income—incentives that drove a 137% increase in food donations when expanded in 2006
- The government also offered grants specifically targeting food waste reduction, including the USDA’s Composting and Food Waste Reduction program, which awarded $10.2M in 2022 alone.
- It also provides R&D tax credits for waste management companies developing innovative upcycling technologies, which are often overlooked but potentially lucrative.
- Meanwhile, emerging regulatory frameworks in the European Union create a favorable environment for upcycled food startups, signaling increased support and funding opportunities.
- Cost-saving advantages from utilizing otherwise wasted ingredients, enhancing profit margins, and business resilience
While early investments focused primarily on consumer-facing upcycled products, capital is increasingly flowing toward platform technologies that can transform multiple waste streams into various high-value ingredients and materials. This infrastructure-level investment signals the maturation of the circular ingredients economy.
Companies Leading the Revolution
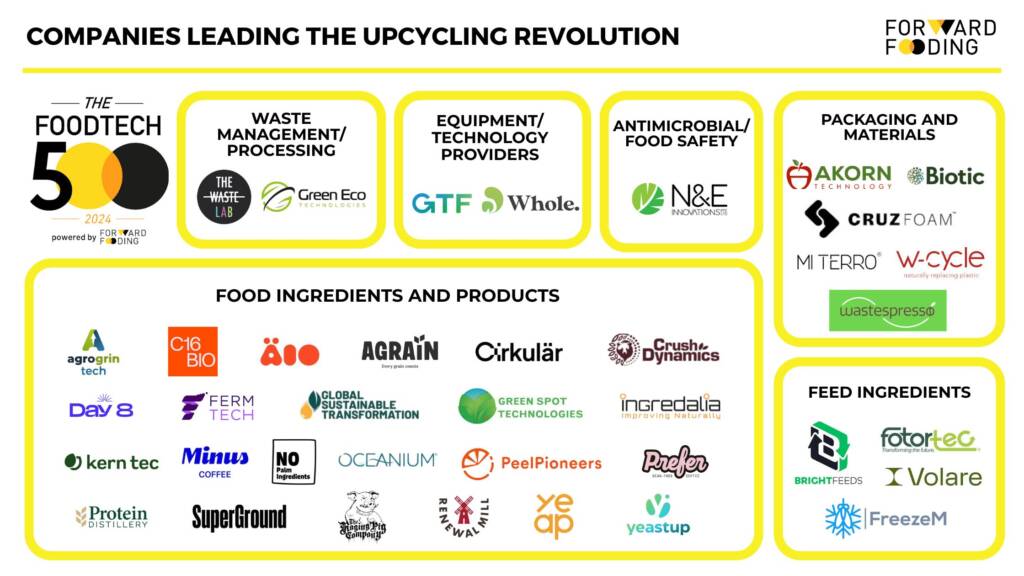
Food Ingredients and Products
Agrogrin Tech (#310 in the 2024 FoodTech 500) | Produces clean-label ingredients made from upcycled fruits and vegetables to meet the market demands of the food, supplement, and cosmetic industries.
Agrain (#285 in the 2024 FoodTech 500) | Upcycles industrial food waste into tasty and healthy products and ingredients such as flour, granola, and snacks.
ÄIO (#198 in the 2024 FoodTech 500) | Creates innovative, healthy, and reliable microbial alternatives to replace unsustainable ingredients like palm oil, coconut oil, and animal fats.
C16 Biosciences (#53 in the 2024 FoodTech 500) | Uses microbiology to brew sustainable alternatives to palm oil.
Cirkulär (#499 in the 2024 FoodTech 500) | Develops cell factories that produce the key ingredients in milk.
Crush Dynamics Inc (#104 in the 2024 FoodTech 500) | Transforms grape derivatives into highly nutritious food ingredients through a patented biomechanical process, aiming to address critical challenges in the food and beverage industries, such as sugar and sodium reduction.
Day 8 (#425 in the 2024 FoodTech 500) | Utilizes a unique extraction method to create Rubisco-based protein ingredients that provide nutritional benefits similar to animal proteins.
Global Sustainable Transformation (#154 in the 2024 FoodTech 500) | Provides its property yeast butter as a sustainable equivalent to cocoa butter
Green Spot Technologies (#85 in the 2024 FoodTech 500) | Provides innovative fermented and upcycled ingredients, particularly flours, that enable food brands to meet the demands of modern consumers while promoting sustainability.
Ingredalia (#330 in the 2024 FoodTech 500) | Transforms plant by-products into natural functional ingredients.
Kern Tec (#175 in the 2024 FoodTech 500) | Turns stone fruit pits into high-quality raw materials like baking ingredients, sustainable cosmetic oils, fertilizers, and biomass.
Minus (#87 in the 2024 FoodTech 500) | Produces beanless coffee.
NoPalm Ingredients (#133 in the 2024 FoodTech 500) | Creates environmentally friendly microbial oils to substitute palm and other tropical oils in food, cosmetics, and detergents. The oil is produced in a sustainable, cyclical, and environmentally beneficial manner through the fermentation of sidestreams.
Oceanium (#195 in the 2024 FoodTech 500) | Develops innovative, all-natural food and nutraceutical products and sustainable materials from sustainably-sourced seaweed.
PeelPioneers (#238 in the 2024 FoodTech 500) | Extracts valuable raw materials from citrus peels, such as Finix Citrus Fiber, which is used in food as a thickener.
Prefer (#361 in the 2024 FoodTech 500) | Creates coffee by fermenting upcycled food by-products from beer, bread, and tofu manufacturing.
Protein Distillery (#116 in the 2024 FoodTech 500) | Produces clean protein ingredients sourced from fermented biomass materials, such as brewer’s yeast.
The Raging Pig Company (#381 in the 2024 FoodTech 500) | Develops and distributes alternative products to pork, such as vegan bacon and German sausage alternative.
Renewal Mill (#145 in the 2024 FoodTech 500) | Upcycles fiber and protein produced during large-scale food manufacturing into high-quality ingredients and products.
SuperGround (#470 in the 2024 FoodTech 500) | Offers a scalable food processing solution that upcycles side-stream materials to produce high-quality food products for a more sustainable future, with customizable plans designed to minimize food waste and reduce emissions.
Yeap (#459 in the 2024 FoodTech 500) | Offers a yeast-based protein source made from industrial side streams that can be used as a functional ingredient, bulking ingredient, or concentrated protein powder.
Yeastup (#94 in the 2024 FoodTech 500) | Upcycles by-products from the beer-brewing process into quality ingredients, thus promoting the circular economy.
Feed Ingredients
Bright Feeds (#199 in the 2024 FoodTech 500) | Transforms food waste into feed using artificial intelligence and drying technology.
FreezeM (#166 in the 2024 FoodTech 500) | Boosts insect protein production by supplying high-performing, life-cycle PAUSED Black Soldier Fly (BSF) neonates at scale, called PauseM
Fotortec (#409 in the 2024 FoodTech 500) | Engages in sustainable protein production as a biotechnology company.
Volare (#131 in the 2024 FoodTech 500) | Upcycles industrial food waste into sustainable protein, oil, and fertilizer ingredients.
Packaging and Materials
Akorn Technology (398 in the 2024 FoodTech 500) | Uses upcycled, non-GMO corn by-products to manufacture edible coatings that make the shelf life of fresh produce last.
Biotic (#323 in the 2024 FoodTech 500) | Provides a circular, fully bio-based, fully biodegradable PHBV (PHA) polymer manufacturing process, and its polymer is applicable for the vast majority of today’s plastic demand, including packaging, disposables, and single-use products.
Cruz Foam (#231 in the 2024 FoodTech 500) | Creates products from naturally sourced biopolymers that create a scalable, compostable alternative using the existing supply chain and at a similar cost.
Mi Terro (#197 in the 2024 FoodTech 500) | Creates ocean-degradable and home-compostable flexible packaging materials made from agricultural waste.
W-Cycle (#497 in the 2024 FoodTech 500) | Develops SupraPulp™, a compostable and non-coated food packaging solution made from 100% natural materials. This innovative packaging is liquid and oil-proof, as well as microwave-, oven-, and freezer-safe, offering a sustainable alternative.
Wastespresso (#240 in the 2024 FoodTech 500) | Produces bioplastic compounds and products from spent coffee grounds, such as disposable and reusable cups, straws, flower pots, and spoons.
Antimicrobial/Food Safety
N&E Innovations (#232 in the 2024 FoodTech 500) | Develops 100% natural antimicrobial compounds that effectively eliminate virulent particles.
Waste Management/Processing
Green Eco Technologies (#462 in the 2024 FoodTech 500) | Supplies and manages unique on-site food waste conversion and repurposing solutions.
The Waste Lab (#322 in the 2024 FoodTech 500) | Provides waste sorting and disposal, which, in turn, will be used to create healthy compost.
Equipment/Technology Providers
Fermtech (#356 in the 2024 FoodTech 500) | Produces delicious, nutritious, zero-carbon protein with a unique fermentation system that uses food industry side streams.
GTF Technologies (#492 in the 2024 FoodTech 500) | Designs and manufactures RENU™ Drying & Milling systems that simultaneously dry and micronize organic materials in seconds, reducing costs and promoting sustainability.
Whole. (#363 in the 2024 FoodTech 500) | Utilizes its proprietary WINXⓒ technology to eliminate waste and enhance bioavailability in all food and beverage processing applications.
Scaling Challenges & Future Outlook
Despite the promising innovations and growth, several challenges must be addressed for circular ingredient technologies to achieve their full potential:
Integration with Existing Systems
Many circular solutions require integration with established food manufacturing operations and legacy systems. Real-world implementations, such as PlanetTogether, showcase how advanced planning and scheduling capabilities can help manufacturers visualize production scenarios with upcycled ingredients, efficiently allocate resources, and optimize throughput without disrupting core processes.
Switzerland-based startup Gaia Tech demonstrates successful integration in practice, having secured CHF 480,000 in pre-seed funding to upcycle food processing and agricultural production sidestreams into clean-label ingredients for cosmetics, food, and feed manufacturers through pilot production with leading industry partners.
Regulatory Evolution
Regulations around novel food ingredients, safety standards for byproduct utilization, and labeling requirements for upcycled products vary widely across regions and are often outdated. A case study on olive leaf extract integration as an upcycled ingredient highlights the “urgent need for clear regulations and standardized guidelines to facilitate the successful adoption” in the food industry.
In response to this need, the Upcycled Food Association developed the world’s first Upcycled Certification Standard in 2021, establishing a framework for food products and ingredients that would otherwise not have been used for human consumption.
Behavior Change
While technology can enable better practices, lasting change requires shifts in behavior from producers to consumers. Research has identified key factors influencing consumer acceptance of upcycled foods, including gender, educational level, food neophobia, environmental awareness, and food waste awareness. The findings show that communicating the positive impacts on health, nutrition, sustainability, and economic benefits can significantly increase consumer acceptance.
Another study across five European countries revealed that “stressing the aspect of traditional frugality” and appealing to “frugal orientation appears a favorable communication frame for upcycled food,” particularly targeting environmentally concerned consumer segments.
Measurement Standardization
The industry still lacks standardised metrics for measuring and reporting the impact of circularity, making it difficult to compare solutions and demonstrate value to potential partners and investors. The Upcycled Certification Program has begun addressing this by requiring information on “the amount of upcycled content within an ingredient or product, the amount diverted as a result of yearly production,” and setting specific thresholds for certification.
This certification has yielded tangible results, with 93 companies and over 480 certified products now responsible for diverting an average of 390,000 tons of food waste annually since the program’s launch.
The Path Forward
Benefits of Circular Food Technologies
The evolution of circular food technologies represents one of the most promising intersections of environmental sustainability and economic opportunity in the food system. By transforming previously discarded materials into valuable ingredients and products, these innovations offer multiple benefits:
- Reduced greenhouse gas emissions – Circular food systems directly address SDG targets 12.3 (food waste reduction) and 13.2 (climate policy integration), with research showing that adopting circular principles in food production systems can significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
- Measurable economic value creation – Circular food pioneers are capitalizing on the “biomass value chain” estimated by the World Economic Forum at $295B annually by 2020, not only reducing environmental impact but also generating significant financial rewards. Experimental analysis and consumer surveys show high public acceptance (81%) of upcycled food products, with consumers showing willingness to pay for processing their food waste, indicating strong marketability potential.
- Verified nutrient recovery and soil regeneration – Companies like Ostara Nutrient Recovery Technology have developed “Pearl Technology” that can recover 85% of phosphorus and up to 15% of nitrogen from wastewater, transforming these recovered materials into high-value fertilizer products for agricultural use.
- Scientifically measured resource efficiency – Life Cycle Assessment studies of circular food initiatives consistently demonstrate significant improvements in resource efficiency metrics, with studies quantifying material flows, waste reduction, and energy conservation alongside global warming potential reductions.
- Quantifiable consumer adoption metrics – According to a 2019 survey, 39% of consumers specifically want to buy upcycled foods, with the Upcycled Food Association certification standard helping to make these products identifiable to interested consumers.
Emerging Trends in Circular Ingredient Innovation
Looking ahead, we anticipate several emerging trends that will shape the next phase of circular ingredient innovation:
1. Precision fermentation applied to diverse waste streams – enabling more sophisticated transformation of residues into specialized ingredients. Startup Hyfe exemplifies this approach by extracting sugar from food manufacturing wastewater, turning it into standardized microbe feed for precision fermentation while simultaneously providing water treatment services for breweries and canning factories.

Meanwhile, Liven Proteins has positioned itself as the first precision fermentation company in Canada that upcycles food waste to produce animal-free collagen and gelatin, using a “proprietary fermentation process” that transforms “lost, or waste, foods, to feed microorganisms that create a side stream.”
2. Functional upcycled ingredients with targeted health benefits – moving beyond basic nutrition to offer bioactive compounds with specific physiological effects. Brightseed has pioneered this approach with their Bio 01 hemp fiber ingredient, which contains two unique bioactives (NCT & NFT) discovered using their AI platform Forager, specifically targeting gut health benefits.

Research also highlights significant potential in upcycling waste from citrus processing, with orange peel extract containing bioactive compounds that help in “delaying skin aging” and reducing “oxidative damage, as well as skin-related issues such as acne, wrinkles, dark spots.”
3. Cross-industry circular collaborations – where one industry’s byproducts become another’s raw materials. London-based Ananas Anam demonstrates this cross-industry approach by upcycling pineapple leaf fibers, a byproduct of pineapple harvests, into Piñatex (leather alternative) and Piñayarn (fiber) used across fashion, automotive, footwear, and interior design industries.

Similarly, Danish startup Kaffe Bueno operates the world’s first coffee biorefinery in Rødovre, Denmark, which can upcycle 500 tons of spent coffee grounds annually into high-value ingredients for cosmetics, nutraceuticals, and functional foods, transforming what would otherwise release harmful methane into valuable products like KAFFOIL for skincare and KAFFIBRE for food applications.

Ready to discover how upcycled food is evolving beyond waste reduction into a powerful business opportunity? Join TransFoodMission in their upcoming webinar on May 23rd at 13:00 CEST with the theme: “From Niche to Mainstream: The Strategic Rise of Upcycled Food in Retail” to gain exclusive insights into the strategic framework that’s poised to make upcycled food a mainstream choice for retailers, manufacturers, and consumers. Register now to secure your spot and be among the first to learn the roadmap for building resilient and high-impact upcycled food categories!
Forward Fooding is the world’s first collaborative platform for the Food & Beverage industry via FoodTech Data Intelligence and Corporate-Startup Collaboration – Learn more about our Consultancy and Scouting Services and our Startup Network.
Follow us
Sponsored Articles
9 July 2025
Forward Fooding celebrates the selection of 12 pioneering startups for the inaugural pladis Accelerator Programme. From water lily popcorn to sugar-converting enzymes, these innovations represent the future of snacking, addressing obesity, sustainability, and personalized nutrition through cutting-edge food technology.
21 March 2025
Tim Ingmire, VP of Global Innovation & Technology at pladis, discusses how the snacking giant is supporting early-stage startups in foodtech, health, and sustainability through their accelerator program. Learn about their focus on personalized nutrition, functional foods, and future ingredients to bring innovative, delicious products to consumers worldwide.
8 February 2024
Future Food-Tech returns to San Francisco on March 21-22 Over 1,700 food-tech leaders, from CPG brands, retailers, ingredient providers, [...]
1 February 2023
The 4th edition of FoodTech 500 is taking off and we are excited to partner with NEOM for the third consecutive year to support the best international AgriFoodTech entrepreneurs.
10 February 2022
One of the elements we enjoy the most here at Forward Fooding about working with AgriFoodTech startups is being [...]






