FORWARD FOODING
THE BLOG
Chocolate’s getting a sustainable makeover

The beloved world of chocolate is facing a seismic shift as climate change and environmental pressures make traditional cocoa production increasingly unsustainable. Cocoa prices are soaring, and the future of this key ingredient looks uncertain. Major players in the chocolate industry are pressed to find innovative cacao alternatives, and consumers may soon experience chocolate made from entirely new ingredients.
Chocolate under media spotlight
Despite its cherished status, the cocoa industry faces significant labor and supply chain issues. Historically known as the “Food of the Gods” and used by the Aztecs in rituals and as currency, cocoa is now often associated with poverty and child labor. Many smallholder farmers in Ghana and Côte d’Ivoire live in poverty, lacking the resources to invest in their farms. A 2021 report from the World Economic Forum revealed that up to 58% of cocoa farmers in these regions live below the World Bank’s extreme poverty line, and up to 90% do not earn a living income. Child labor remains pervasive, with an estimated 1.56 million children involved in cocoa production in Côte d’Ivoire and Ghana.
While organizations like Fairtrade International and Rainforest Alliance provide valuable training and investment to cocoa farmers, aiming to improve their income and working conditions, significant hurdles remain. Inadequate enforcement of certification standards and the mixing of certified and non-certified beans weaken the impact of these efforts.
Despite initiatives like Nestle’s Income Accelerator Programme that aim to address income challenges- many farmers continue to face difficulties in achieving a living income. Traceability issues and a lack of robust enforcement mechanisms continue to plague the cocoa supply chain.
Furthermore, the environmental impact of cocoa farming is significant, with dark chocolate being one of the top greenhouse gas-emitting foods, second only to beef. Global warming threatens cocoa crops, with scientists warning that a third of them could die out by 2050, potentially causing a global chocolate shortage. Ageing cocoa trees, which become less productive over time, further exacerbate this decline. The Cocoa Board of Ghana has emphasized the need for rejuvenating cocoa farms with high-yielding, disease-resistant varieties.
Innovative Alternatives: Cocoa-Free Chocolate and Cell-Based Chocolate
The rise of technology in the food industry has given birth to new players who are disrupting the traditional cocoa supply chain. These technological advancements are not only addressing the immediate supply chain issues but are also paving the way for a more sustainable and ethical chocolate industry. Two key technologies have emerged as particularly noteworthy: cell-based and fermentation-based methods.
New technologies on our watch
Fermentation
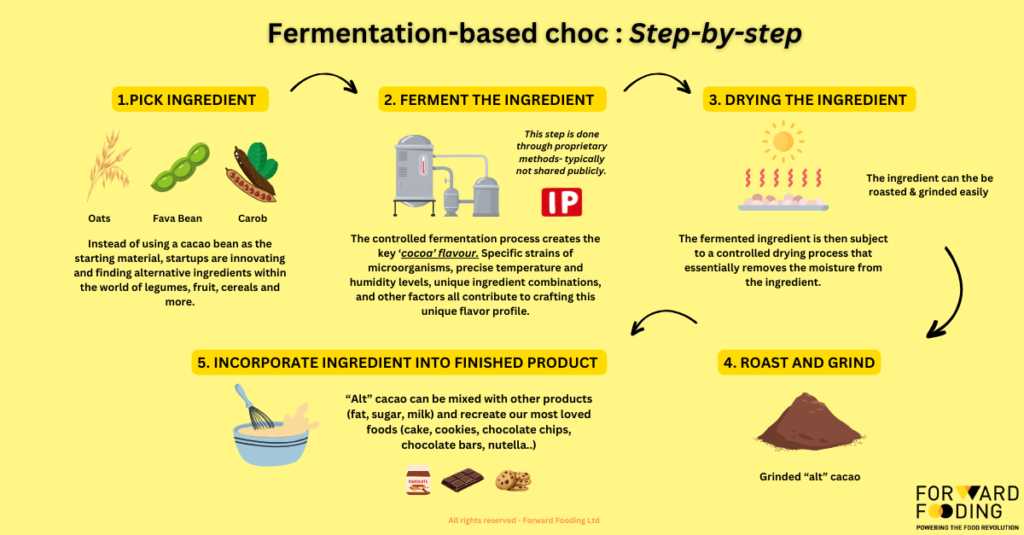
Ingredients like carob and fava beans undergo a controlled fermentation process akin to traditional methods. This involves microorganisms such as lactic acid bacteria and yeast, which ferment the sugars. The duration and specific conditions like temperature and humidity are adjusted to achieve desired results. Check out the step-by-step process below:
1- Pick Ingredient
Instead of traditional cacao beans, alternative ingredients such as oats, fava beans, and carob are selected. Startups innovate by finding new ingredients from legumes, fruits, cereals, and more, which serve as the base for fermentation.
2- Ferment the Ingredient
The chosen ingredient undergoes a controlled fermentation process. This involves using specific strains of microorganisms and maintaining precise temperature and humidity levels to develop the unique “cocoa” flavor. This proprietary process is not typically disclosed in detail.
3- Dry the Ingredient
After fermentation, the ingredient is dried. This process removes moisture, making the ingredient suitable for further processing (roasting and grinding).
4- Roast and Grind
The dried ingredient is then roasted to enhance its flavor profile. After roasting, it is ground into a fine powder, similar to traditional cacao processing, to prepare it for incorporation into various chocolate products.
5- Incorporate Ingredient into Finished Product
The ground “alt” cacao is mixed with other ingredients such as fat, sugar, and milk to recreate popular chocolate products like cakes, cookies, chocolate chips, chocolate bars, and spreads. This final step ensures that the fermentation-based chocolate mimics the taste and texture of traditional chocolate products.
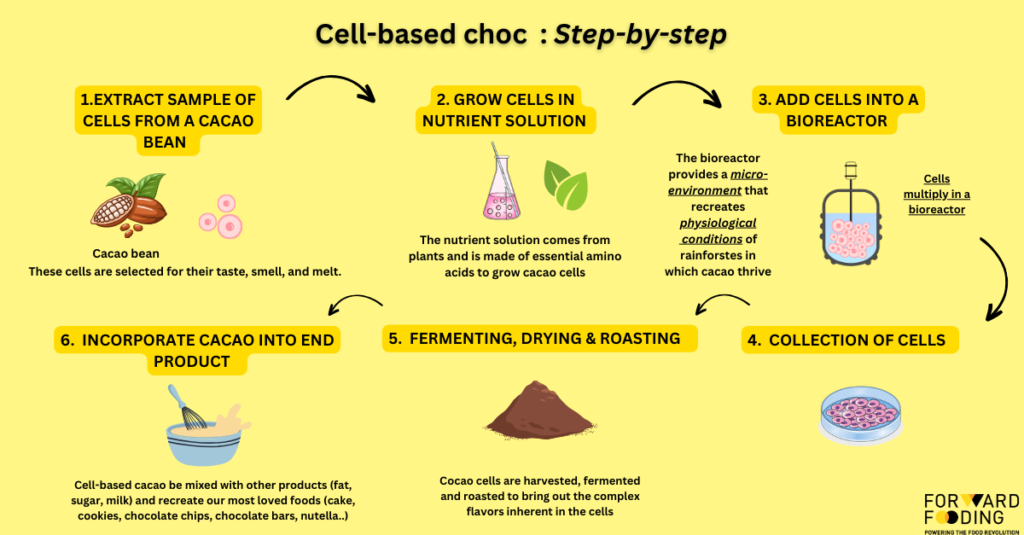
Cell-based chocolate
Cell-based cacao is produced by isolating cells from cocoa plants and cultivating them in a nutrient-rich medium in bioreactors. These cells grow and differentiate to produce the desired cocoa compounds, such as cocoa butter and cocoa solids.
Check out the step-by-step process below:
1- Extract Sample of Cells from a Cacao Bean
Cacao beans are carefully selected for their desirable traits such as taste, smell, and melting properties. A sample of cells is extracted from these beans.
2- Grow Cells in Nutrient Solution
The extracted cells are placed in a nutrient-rich solution. This solution contains essential amino acids and other nutrients derived from plants, which are necessary for the growth and development of cacao cells.
3- Add Cells into a Bioreactor
The cells are transferred to a bioreactor, a device that creates a controlled environment mimicking the natural conditions of a rainforest. This bioreactor provides the optimal physiological conditions for cacao cells to thrive and multiply.
4- Collect Cells
Once the cells have grown and multiplied sufficiently, they are collected from the bioreactor.
5- Ferment, Dry, and Roast Cells
The harvested cacao cells undergo fermentation, a process that enhances their flavor profile. After fermentation, the cells are dried and roasted to develop the complex flavors inherent in cacao, similar to traditional chocolate production.
6- Incorporate Cacao into End Product
The final step involves incorporating the processed cacao cells into various products. These can include mixing with fat, sugar, milk, and other ingredients to recreate beloved chocolate products such as cakes, cookies, chocolate chips, chocolate bars, and nut spreads.
Key benefits & bottlenecks of alt-chocolate
Unlike conventional chocolate production, alt-chocolate boasts a much smaller environmental footprint. Fermentation and plant-based alternatives can dramatically reduce carbon emissions (up to 99% lower!), deforestation, and water usage. By making use of traditional fermentation, no regulatory approval is required, giving fermentation-derived companies an advantage.
Some alt-chocolate options go beyond just satisfying the consumer’s sweet tooth. Products like Nukoko’s fava bean chocolate offer a healthier twist with less sugar and a boost of protein, fiber, and antioxidants naturally found in the beans.
While the future looks promising, alt-chocolate still faces some hurdles. Regulatory approval remains a challenge, especially for cellular agriculture products. To this day, California Cultured is working towards obtaining GRAS (Generally Recognized as Safe) certification from the US FDA. Although cocoa cells are simpler to grow compared to cultivated meat and require less complex media, the economic viability remains a challenge. However, here it’s important to note that only a small percentage of chocolate will be included in packaged goods, which could limit the impact of high production costs on the final price. The final challenge is around taste. Replicating the rich and complex taste of traditional chocolate can be a challenge for fermentation-derived chocolate; and limit consumer adoption.
Key startups to watch
According to the FoodTech Data Navigator, we map 21 startups & scaleups working in the field of alternative cacao/chocolate. Since 2014, total funding towards these technologies reached 309 million in capital raised and has recorded a CAGR of 100% (2018-2023); explained by rising cocoa prices, supply constraints, and increasing demand for sustainable alternatives.

Voyage Foods is an innovative food technology company focused on creating sustainable, eco-friendly alternatives to traditional food products. Their flagship product is cocoa-free chocolate, which replicates the taste and texture of conventional chocolate using non-cocoa ingredients like grape seeds from post-harvest wine production combined with vegetable oil, cane sugar, and sunflower protein flour. Voyage Foods has raised $115 million in total funding across four rounds. The most recent Series A round in April 2023 secured $43 million, aimed at scaling production and expanding their product line. More notably, Voyage Foods partnered with agricultural giant Cargill to scale up production of cocoa-free chocolate products in 2024.

Planet A Foods, founded in 2021 specializes in creating sustainable cocoa alternatives. The company’s innovative product,ChoViva, is made from locally sourced ingredients like oats and sunflower seeds using proprietary fermentation technology. They also use precision fermentation to produce a cocoa butter equivalent. Planet A Foods recently secured $15.4 million in a Series A funding round, bringing their total funding to over $28 million. Planet A Foods has successfully scaled its production processes and launched products in the UK and Germany. In 2023, Planet A Foods expanded its ChoViva cocoa-free chocolate, collaborating with major brands like REWE and Lindt.
Celleste Bio produces 100% natural cocoa butter and powder without deforestation, ensuring a sustainable, scalable, and high-quality cocoa supply. Celleste Bio’s latest funding round was a Seed Round in 2022 – backed by investors including the likes of Mondelez International, and other strategic partners to support scaling production.
Kokomodo is an innovative Israeli startup specializing in lab-grown cocoa and chocolate products. Using state-of-the-art bioreactors, Kokomodo cultivates premium cocoa cells sourced from Central and South America, ensuring sustainability and high quality for the food, beverage, supplements, and cosmetics industries. Kokomodo recently secured $750,000 in funding from The Kitchen FoodTech Hub and the Israeli Innovation Authority; and will be used to work towards commercial viability.
California Cultured is a food-tech company based in Davis, California, that uses cell culture technology to produce cocoa products such as cocoa powder, chocolate, cocoa butter, and flavanols. California Cultured recently raised $4 million in a Seed Funding Round led by Agronomics. In 2024, California Cultured entered into a partnership with Japanese chocolate maker Meiji.

Nukoko, based in Guildford, UK, is a pioneering company that has developed a cocoa-free chocolate bar. Using a unique fermentation process, Nukoko transforms fava beans into a sustainable, nutritious, and delicious chocolate alternative. Founded in 2022 by Ross Newton, Kit Tomlinson, and cocoa research scientist Professor David Salt, the company aims to address environmental and ethical issues in traditional cocoa production while providing a healthier chocolate option. Nukoko recently secured over €1.3 million in Seed funding led by Oyster Bay Venture Capital, with participation from SOSV and The Mills Fabrica.
Win-Win is a London-based startup that creates cocoa-free chocolate alternatives. Using traditional fermentation techniques, Win-Win produces chocolate from fermented barley and carob, combined with shea fat from Ghana. This process replicates the taste and texture of chocolate while being ethical and sustainable. Win-Win secured $5.6 million in a Series A funding round in 2023.
Foreverland, based in Italy, is pioneering the development of cacao-free chocolate using carob as the primary ingredient. They combine this with a mix of various grains, sugar, and vegetable fats that are friendly to clean labeling. Their flagship product, Freecao, is a vegan, gluten-free, caffeine-free chocolate alternative that is also free from the top nine allergens. With successful fundraising of $180,000, Foreverland is scaling up production and further advancing its sustainable chocolate alternative.
Forward Fooding is the world’s first collaborative platform for the Food & Beverage industry via FoodTech Data Intelligence and Corporate-Startup Collaboration – Learn more about our Consultancy and Scouting Services and our Startup Network.
Follow us
Sponsored Articles
9 July 2025
Forward Fooding celebrates the selection of 12 pioneering startups for the inaugural pladis Accelerator Programme. From water lily popcorn to sugar-converting enzymes, these innovations represent the future of snacking, addressing obesity, sustainability, and personalized nutrition through cutting-edge food technology.
21 March 2025
Tim Ingmire, VP of Global Innovation & Technology at pladis, discusses how the snacking giant is supporting early-stage startups in foodtech, health, and sustainability through their accelerator program. Learn about their focus on personalized nutrition, functional foods, and future ingredients to bring innovative, delicious products to consumers worldwide.
8 February 2024
Future Food-Tech returns to San Francisco on March 21-22 Over 1,700 food-tech leaders, from CPG brands, retailers, ingredient providers, [...]
1 February 2023
The 4th edition of FoodTech 500 is taking off and we are excited to partner with NEOM for the third consecutive year to support the best international AgriFoodTech entrepreneurs.
10 February 2022
One of the elements we enjoy the most here at Forward Fooding about working with AgriFoodTech startups is being [...]






